Stud Bolt – A complete Guide of Pipe Fasteners
Stud bolt, nuts, machine bolts, and washers are also known as bolting material or fastener. Bolting is the term that used to tighten/create the flange joints connection. The tightening of the flange ensures the leak-proof connection between gasket & flanges.
ASME flanges have a minimum four bolt hole and for higher diameter flanges, the number of bolt holes is always in multiples of four. Selection of number bolt holes depends on the factor such as
- Size of the flange
- Working pressure
- Working temperature
- Flange material
Different Kinds of Fasteners Used in Piping
Stud Bolt
The stud has a thread on full-lengths or at both ends. As shown in images. It is having three components if washers are not used (two nuts and stud). If you used washer it would become five. Sometimes additional nuts are used for hydraulic tensioning with larger size stud.
The length of the stud bolt should be enough to cover the entire Nut plus 1.5 to 3 threads exposed. Long studs must be avoided as it increases the chance of corrosion and other damage to exposed threads, which would make subsequent removal difficult.
ASME B16.5 gives the required size of the stud. The length of the stud depends on the type of gasket and the maximum exposed thread requirements.
Machine Bolt
Bolts have a thread at one end and hexagonal head on another end. See the image below. In the process, piping bolts are used with lower strength flange types such as GRE/GRP, bronze. Usually, washers are used with a bolt to prevent excessive load to the flange.
Nuts
Commonly Hexagonal Heavy-series nuts used with studs. The nonbearing face of a nut is chamfered, while load Bearing face is finished with a washer face or may be chamfered.
Washers
A washer is a thin plate with a hole at the center. Washers distribute the load on flange face; this prevents damage to the flange. Non-metallic flange required washers due to this reason. Different types of washers are used such as Flat, Splits, and Conical Springs. Flat and split washers are shown in the image.
Conical washers are special washers. Also known as Belleville Springs washers. It Keeps bolted joints tight in an area where vibration, differential thermal expansion, and bolt creep exist.
These conditions can change the load on a stud which may result in a loose connection. Conical washers provide a spring effect and prevent the loosening of a stud. This washer provides High spring loads with small deflections.
Stud Bolt Specification & Standard
Various ASME standards are used for stud bolts and nuts to manufacturing bolting material. A list of such standards is given below.
- Diameter and Lengths of the stud and bolt are covered in ASME B16.5 & B16.47
- ASME B1.1 Unified Inch Screw Threads (Cores and Fine thread series- normally Cores thread series is used for stud used in piping)
- ASME B18.2.1 for Square and Hex Bolts and Screws
- ASME B18.2.2 Square and Hex Nuts
- ASME B18.21.1 Lock Washers
- ASME B18.22.1 Plain Washers
Stud Material Grades
Bolting material can be divided into three group
- High Strength
- Intermediate strength
- Low Strength
Stud Materials
A list of ASTM Material grades used for manufacturing stud is given in ASME B16.5, which is the Standard for the flanges.
- High temperature and pressure services ASTM A193 Gr B7, B7M, B5, B8 are used.
- Low-temperature services ASTM A320 Gr L7, L7A, L7B are used.
- Alloy steel quenched and tempered studs and bolts material grades are ASTM A354 Gr BC, BD.
- For special application, ASTM A540 Gr B21 to B24 are used.
Out of these grades, the most popular material grades are ASTM A193 Gr B7 & B7M.
Nuts Materials
Nuts may be machined from the same material as a stud or maybe of a compatible grade of ASTM A194
- ASTM A194 standard lists the compatible material grades for nuts that used with stud & bolt.
- Most widely used material grades are ASTM A194 Gr 2,2H,2HM,8,8M
Washer Materials
The common material grade used for washer manufacturing are
- ASTM F436, ASTM F844, ASTM F959
- If not specified washer can be manufactured from any compatible grade material
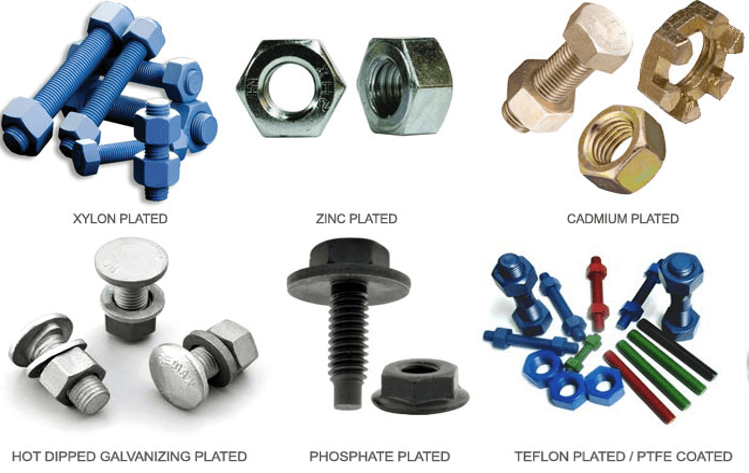
Coating on Stud Bolts and Nuts
Sometimes Bolting components are coated with different coating materials to improve its corrosion resistance. This will reduce maintenance costs. Common coatings are
- Chrome Plating
- Galvanizing
- Xylan
- PTFE
- Zinc
You can see these coating in the image.
Inspection of stud bolts
During a visual inspection, Check for any surface defect and overall product quality
- Check for Damage thread & Poor chamfered of a head of nuts and ends of the stud
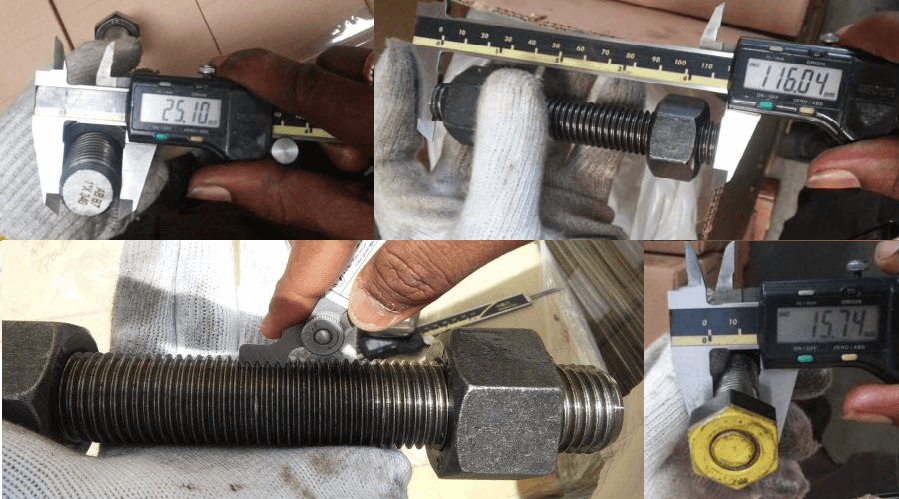
Following to be confirmed during dimension inspection of the stud bolts
- Thread pitch
- Diameter of stud and bolt
- Length
- Dimension of Bolt head and Nuts
Marking requirements
Stud Marking
Marking requirements for stud & bolt are specified in ASTM material Standard A193 and A320. Marking to be done at the ends of the stud or on the bolt head. Due to limited space only, the Manufacturer’s identification mark & Material Grade / Class are marked on stud and bolt.
ASTM standard gives the list of marking symbols for various material grades. Check the image below ASTM A193 Gr B7M just marked as B7 at one end and Manufacturer’s identification mark on other ends. In the case of hex head bolt, both the symbols are marked on the bolt head.
Nut Marking
Material Standard ASTM A194 and A563 specify marking requirements for nuts. Marking to be done on the nut’s non-load bearing face. Only the Manufacturer’s identification mark and Material Grade / Class are marked.
Instead of full material description material symbol is used as shown above. The list of symbols is given in the ASTM standard.
What is Hot Bolting?
The removal of flange bolts on the live line and equipment that means when the plant is running is known as hot bolting. There are many reasons for hot bolting such as
- Replacing corroded or damaged bolts
- Upgrading the material specification/grades of bolts
- Minimize the time spent freeing bolts during plant shutdown
Hot bolting is a hazardous activity and utmost care is necessary while performing the same.